
livingandnonlivingthingchart1 Your Home Teacher
Kingdoms of Living Things In his classification scheme, Linnaeus recognized only two kingdoms of living things: Animalia and Plantae. At the time, microscopic organisms had not been studied in detail. Either they were placed in a separate category called Chaos or, in some cases, they were classified with plants or animals.

Pin by Kelly Lee Conner on First Grade Kindergarten anchor charts, Kinder science, Anchor charts
Centuries ago, living things were classified as either plants or animals. Today, the classification of living things helps us gain a better understanding of the world we live in, our relation to living things, and understanding Biology better overall.

CLASSIFICATION OF LIVING THINGS
Classification system. In the 18th century, Carl Linnaeus published a system for classifying living things, which has been developed into the modern classification system. People have always given names to things that they see, including plants and animals, but Linnaeus was the first scientist to develop a hierarchal naming structure that.
Classification of Living Things michelleburden
An interactive map of the evolutionary links between all living things known to science. Discover your favourites, see which species are under threat, and be amazed by the diversity of life on earth. Our tree of life explorer is designed to be easily accessible for everyone. We also provide educational tools for teachers, software for.

Teach the characteristics of living things with this free resource that includes visual notes, a
The term living thing refers to things that are now or once were alive. A non-living thing is anything that was never alive. In order for something to be classified as living, it must grow and develop, use energy, reproduce, be made of cells, respond to its environment, and adapt.

Kindergarten SuperKids March 2012
taxonomy, in a broad sense the science of classification, but more strictly the classification of living and extinct organisms—i.e., biological classification.

Living Things Chart Bell 2 Bell
Living things have a level of complexity and organization not found in lifeless objects. At its most fundamental level, a living thing is composed of one or more cells. These units, generally too small to be seen with the naked eye, are organized into tissues. A tissue is a series of cells that accomplish a shared function.

Chalk Talk A Kindergarten Blog Basic Needs Science lessons, Science activities, First grade
The classification of living things into animals and plants is an ancient one. Aristotle (384-322 BC) classified animal species in his History of Animals, while his pupil Theophrastus ( c. 371 - c. 287 BC) wrote a parallel work, the Historia Plantarum, on plants. [7]
PPT Classification of Living Things PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3139947
Living things are divided into five kingdoms: animal, plant, fungi, protist and monera. Living things are divided into five kingdoms: animal, plant, fungi, protist and monera. Nobody knows for certain when, how or why life began on Earth, but Aristotle observed 2,400 years ago that all the planet's biodiversity was of animal or plant origin.

Classification of Living Things Chart Classification How it Works Exploring Nature
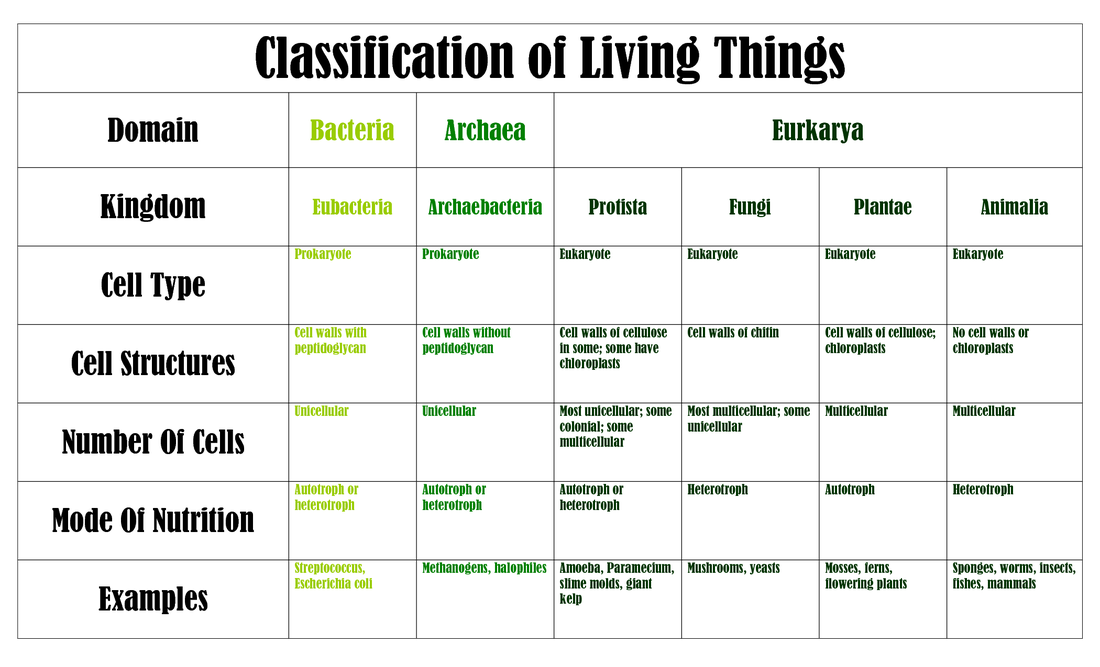
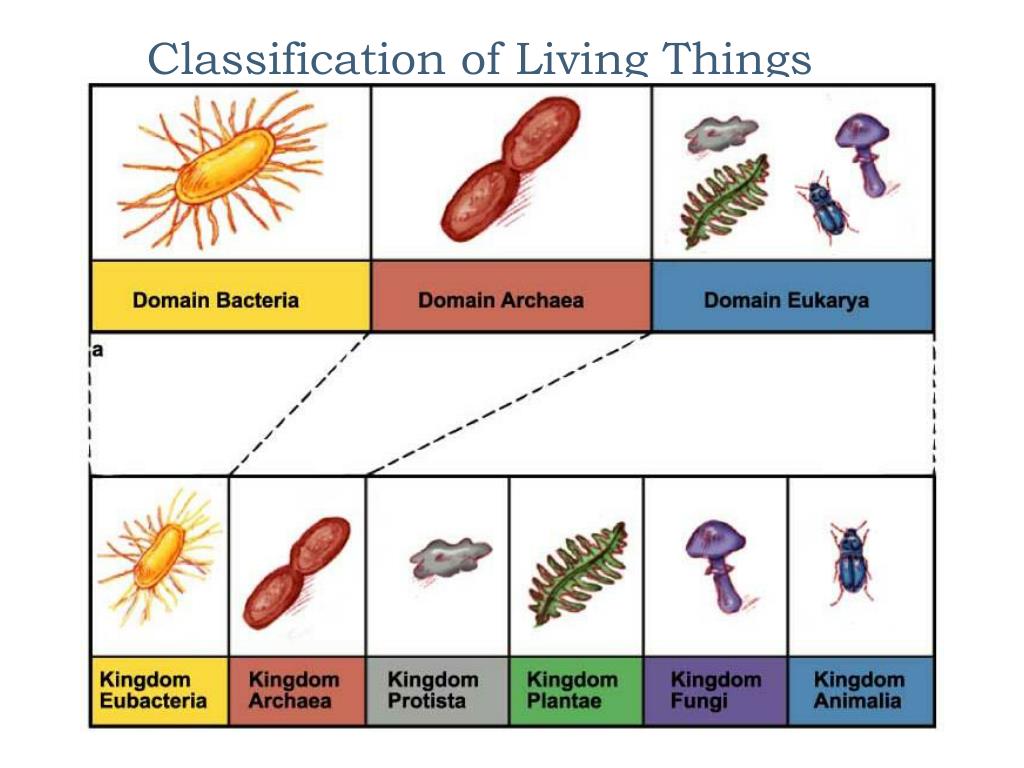
< General Biology | Classification of Living Things Fundamental classification Contents 1 Classification of Living Things and Naming of Organisms 1.1 Binomial nomenclature 2 Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes 3 Three Domains and Six Kingdoms 3.1 The Six Kingdoms 4 Origins of Diversity 5 Phylogeny, Cladistics, and Cladograms

Living and Nonliving Things Mrs. Richardson's Class
Taken together, all of these levels comprise the biological levels of organization, which range from organelles to the biosphere. Figure 1.8.1 1.8. 1: Biological Levels of Organization: The biological levels of organization of living things follow a hierarchy, such as the one shown. From a single organelle to the entire biosphere, living.

Living and non living things powerpoint 1
Class - Sharks & Rays - Cartilaginous Fishes (Grade K-2) Classification of Humans - (4th Grade and up) Ocean Invertebrate Color Poster. Phylum - Cnidaria (Jellyfish, Anemones, Corals, Hydras) Phylum - Echinodermata (Starfish, Sand Dollars, Sea Urchins) Phylum - Mollusca (Gastropods, Bivalves, Cephalopods)

PPT Classification of Living Things PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3652746
He tried to classify all living things that were known at his time. He grouped together organisms that shared obvious physical traits, such as number of legs or shape of leaves.. This chart shows the taxa of the Linnaean classification system. Each taxon is a subdivision of the taxon below it in the chart. For example, a species is a.

LESSON 3 ready. set. classify! BOBCAT SCIENCE
The table below describes seven characteristics of most living things and contains references to earthworms to explain why we can definitely say that they are 'living'. Further classification Based on the information above, we can confidently categorise earthworms as living things as they carry out all seven life processes.

Tales From a K1 Classroom Living and NonLiving
Living things are highly organized and structured, following a hierarchy that can be examined on a scale from small to large. The atom is the smallest and most fundamental unit of matter. It consists of a nucleus surrounded by electrons. Atoms form molecules.

Living and Nonliving anchor chart Kindergarten Resources Pinterest Anchor charts, Chart
Living things are highly organized, meaning they contain specialized, coordinated parts. All living organisms are made up of one or more cells, which are considered the fundamental units of life. Even unicellular organisms are complex! Inside each cell, atoms make up molecules, which make up cell organelles and structures.